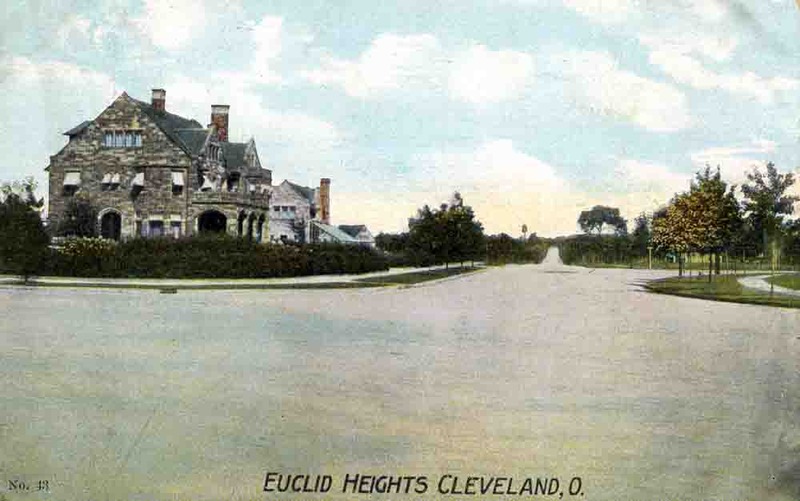
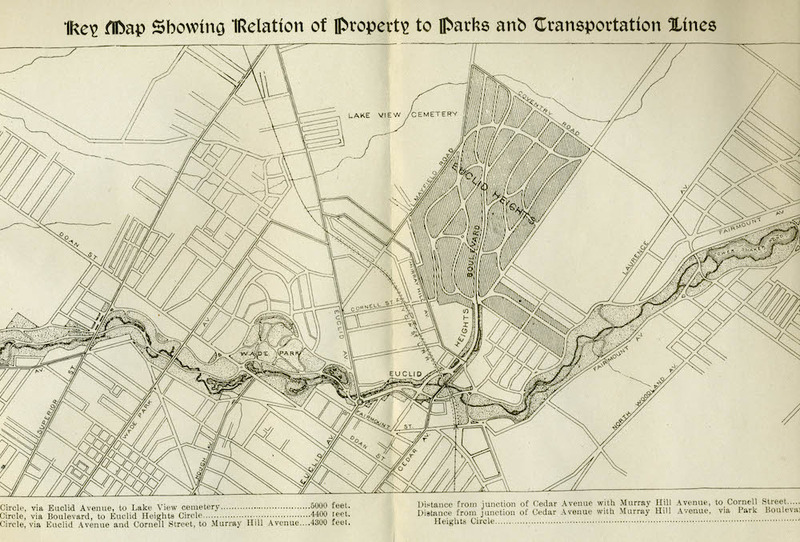
The Euclid Heights Allotment was the first major real estate subdivision up on Cleveland's "Heights" above University Circle and Euclid Avenue. Early on, Euclid Heights’ developers sought to attract wealthy Millionaires’ Row residents who, in the late 19th century, had begun migrating eastward away from the city's pollution and commercial bustle. The development benefited from the advent of electrified streetcars, which could conquer the steep grades leading up to the Heights. Tucked in the corner of a green space framed by Doan Brook and Lake View Cemetery, Euclid Heights offered a stylish retreat where those able to handle longer commutes could enjoy spacious lots, curving streets, handsome architecture, spectacular views, fresh air, privacy and a chance to put distance between themselves and the increasingly dirty, problem-plagued city below.
The story goes that Atlanta and New York railroad lawyer Patrick Calhoun, grandson of U.S. Vice President and Senator John C. Calhoun, traveled to Cleveland on business in 1890. Having time to spare, Calhoun rode out to Lake View Cemetery to see the recently dedicated memorial to the slain President James A. Garfield, a structure Calhoun’s family had supported. On the way he noticed the building boom going on in the East End (Hough area), and wondered where that was heading. Calhoun had been involved earlier in the Richmond Terminal railroad project in Virginia and was familiar with the groundbreaking work that Frank Sprague, the "Father of Electric Traction," had done there in using electric railroads to promote urban development. Knowing that the East Cleveland Railway Company had recently done some innovative work electrifying streetcars locally, Calhoun saw an opportunity to develop an important streetcar suburb at the top of Cedar Glen.
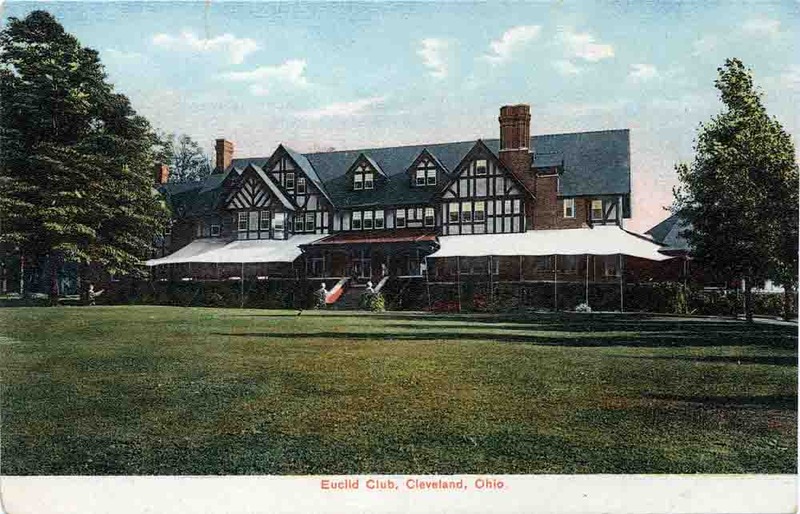
Working with local partners, including John D. Rockefeller's real estate man, J.G.W. Cowles, attorney William Lowe Rice and merchant John Hartness Brown, Calhoun had development plans drawn up by 1892. The Panic of 1893 put their plans on hold but by 1896 an amended site plan was recorded—more or less identical to today's layout of the area with Euclid Heights Boulevard bisecting the site from the southwest corner at the crest of Cedar Hill. In the northeast corner of the development would be the commercial district, what we now know as Coventry Village. Other prominent features included The Overlook—Overlook Road southwest of Edgehill Road and featuring large mansions featuring splendid north- and west-facing views—and the Euclid Club, a country club that sported a golf course spanning both sides of Cedar Road and a grand quarter-mile entry path beginning at what is now the corner of Derbyshire and Surrey Roads.
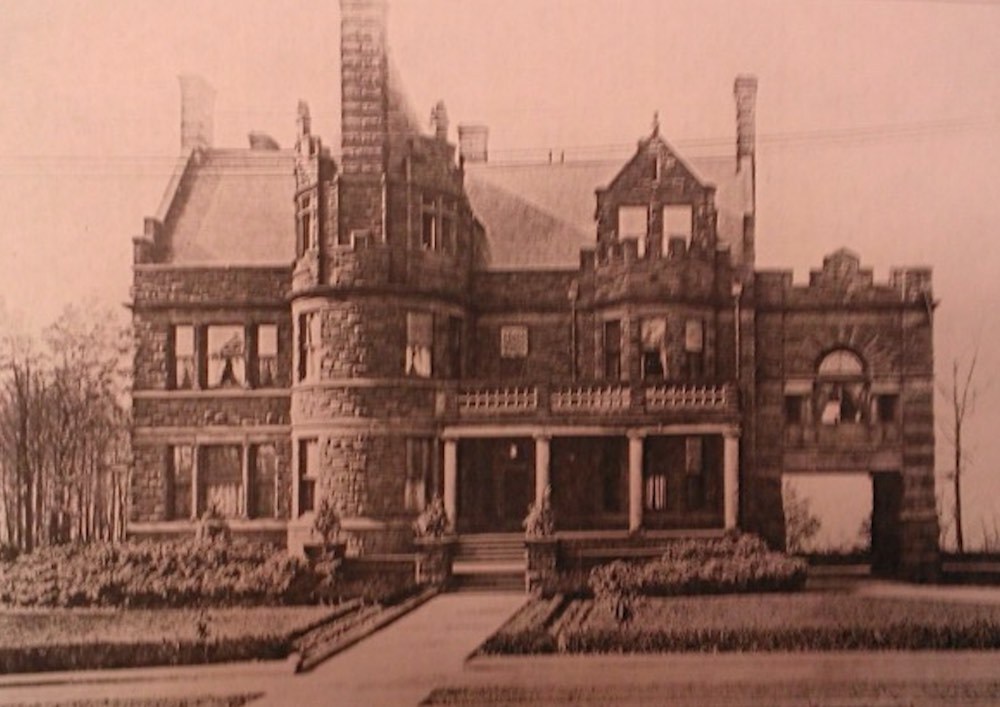
The development gradually attracted fine homes and also spurred other beautiful subdivisions, such as Barton Deming’s Euclid Golf Allotment on the south portion of the former golf course (which closed in 1912). Moreover, the Van Sweringen brothers, are believed to have been paperboys in the Euclid Heights area and later went on to adopt themes from the Euclid Heights Allotment in their famous Shaker Heights and Shaker Farm communities (the latter comprises streets such as Stratford, Marlboro, Fairfax and Guilford, west of Lee Road and immediately north of Fairmount Boulevard) . Calhoun, however, was distracted by legal problems running the San Francisco streetcar franchise after the Great Earthquake and saw his Euclid Heights development company forced into bankruptcy in 1914. By then William Rice had been murdered while walking home to the Overlook from the Euclid Club, a sensational case that featured John Hartness Brown as a suspect. Although it still maintains its picturesque “Garden City” look, Euclid Heights soon evolved from a private hilltop retreat to a busy gateway to the rapidly developing Heights. A large portion of Calhoun-owned land in the area’s eastern sector was sold off and subdivided, thus explaining why Cleveland Heights homes east of Coventry Road tend to be somewhat more modest than those near the top of the hill. Today Euclid Heights is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It remains full of architecturally significant homes (including Calhoun's at 2460 Edgehill), but its main significance is the role it played in opening the Heights as a streetcar suburb for wealthy Clevelanders.
Images